Carpet Beetles
 One
of North Carolina's most common household insects is
the carpet beetle. There are several species, but
the most familiar are the black and the varied
carpet beetle.
One
of North Carolina's most common household insects is
the carpet beetle. There are several species, but
the most familiar are the black and the varied
carpet beetle.
The brown, hairy larvae or cast skins of carpet
beetles usually are found in stored woolens,
carpeting, lint accumulations, cracks and corners of
closets, dresser drawers, and occasionally, in
stored food and cupboards. The larvae are quite
active and may appear almost anywhere in the house.
It is probable that every home has some carpet
beetles, although finding just a few is not usually
considered a problem.
 Adult
carpet beetles are small, oval, black, and
approximately
1/8-inch long. The adult beetles feed on
pollen. The larvae often feed on lint but can cause
serious damage by feeding on animal fibers—wool,
fur, feathers, hair, bristles, mohair—in clothing,
carpeting, upholstery, and other household
furnishings. They do not feed on synthetic fabrics.
Carpet beetles can also be pests in dried food
products, such as flour, corn meal, cereal, and
other similar foods.
Adult
carpet beetles are small, oval, black, and
approximately
1/8-inch long. The adult beetles feed on
pollen. The larvae often feed on lint but can cause
serious damage by feeding on animal fibers—wool,
fur, feathers, hair, bristles, mohair—in clothing,
carpeting, upholstery, and other household
furnishings. They do not feed on synthetic fabrics.
Carpet beetles can also be pests in dried food
products, such as flour, corn meal, cereal, and
other similar foods.
Prevention
Housekeeping is important. Regular, thorough removal
of lint eliminates insect breeding places. Pay
particular attention to rugs, carpets (especially
next to walls), upholstered furniture, closets,
shelves, radiators (and the space under and behind
them), registers and ducts, baseboards, moldings,
corners, and floor cracks.
Inspect clothing and storage areas in the fall and
spring for potential infestations. Also periodically
check that windows and air ducts are properly
screened to help prevent the entry of insects.
Dry clean or launder clothing before storing as
carpet beetles are more apt to infest soiled
material. Store clothing in tight boxes or chests.
It is generally not advisable to use plastic bags.
Although they may not harm clothing during
short-term storage (several months) long-term
storage could result in damage to clothing due to
moisture problems or potential reactions between the
plastic and the fabric.
Place mothballs or crystals (naphthalene) or part of
a no-pest strip (dichlorvos) with the clothes in
storage container. The smell of naphthalene may be
difficult to remove from clothing. Dry clean
clothing again before wearing to help remove any
odor. No-pest strips may be difficult to find in
stores. Cedar chips, although popular as an insect
repellent, do not effectively deter carpet beetles.
Get rid of or properly store remnants or scraps of
wool, fur, fleece, and other material.
Woolen garments and less expensive furs can be
stored in a closet used for that purpose only. A
no-pest strip hung in a closed closet will protect
the garments for 3 to 4 months. One no-pest strip
protects 1,000 square feet. Cut it into smaller
pieces if the storage area is smaller. Do not use
scissors or knives used to cut no-pest strips on
food or food packaging.
Clothes Moths
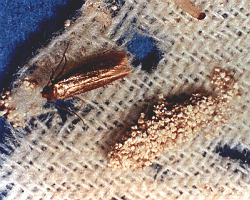 Clothes
moths are well-known pests of fabrics in the home.
Two species of clothes moths commonly infest woolens
and other animal fibers.
Clothes
moths are well-known pests of fabrics in the home.
Two species of clothes moths commonly infest woolens
and other animal fibers.
Both the webbing clothes moth and the casemaking
clothes moth are similar in appearance. The adult
moths are uniformly yellowish or buff in color and
approximately
1/4-inch long. They have a fluttery flight
and tend to avoid light. Fully grown larvae are
1/2-inch long and white with brownish-black
heads. They spin a silken feeding tube or hard
protective case in the fabrics on which they feed.
 The
Indian meal moth, a common house-infesting moth,
often is confused with the clothes moth. However, it
does not attack clothing but rather is associated
with dried food. Indian meal moth adults are darker
on one half of the body.
The
Indian meal moth, a common house-infesting moth,
often is confused with the clothes moth. However, it
does not attack clothing but rather is associated
with dried food. Indian meal moth adults are darker
on one half of the body.
The adult clothes moth lays its soft, white eggs in
the fabric it attacks. The eggs hatch into
creamy-white larvae. The larval stage is the only
feeding stage in the moth's life cycle.
Approximately four generations per year occur under
household conditions.
Most clothes moth infestations in homes are carried
in on carpeting, woolen goods, furniture, and other
home furnishings. Used household items should be
thoroughly sunned before being taken into the home.
Winter clothing should be dry cleaned and stored in
clothing cases or chests between cold weather use.
In general, prevention measures for carpet beetles
also will control clothes moths.
